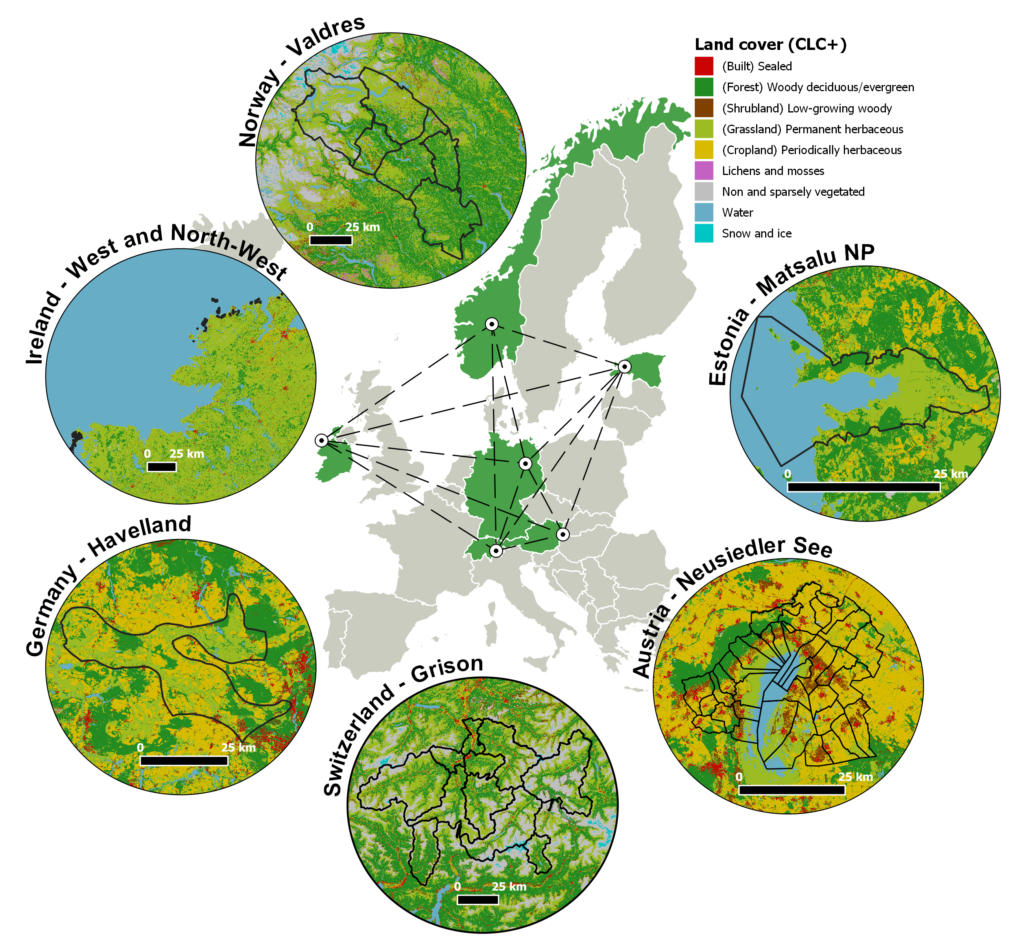
GreeNet applies its concepts and methods empirically in six case studies. The case studies have been selected along a gradient of protection status from highly valuable but yet unprotected landscapes, to protection of single patches within a matrix of agricultural land (e.g. biosphere reserve, Natura 2000 areas), to strongly protected areas such as national parks.
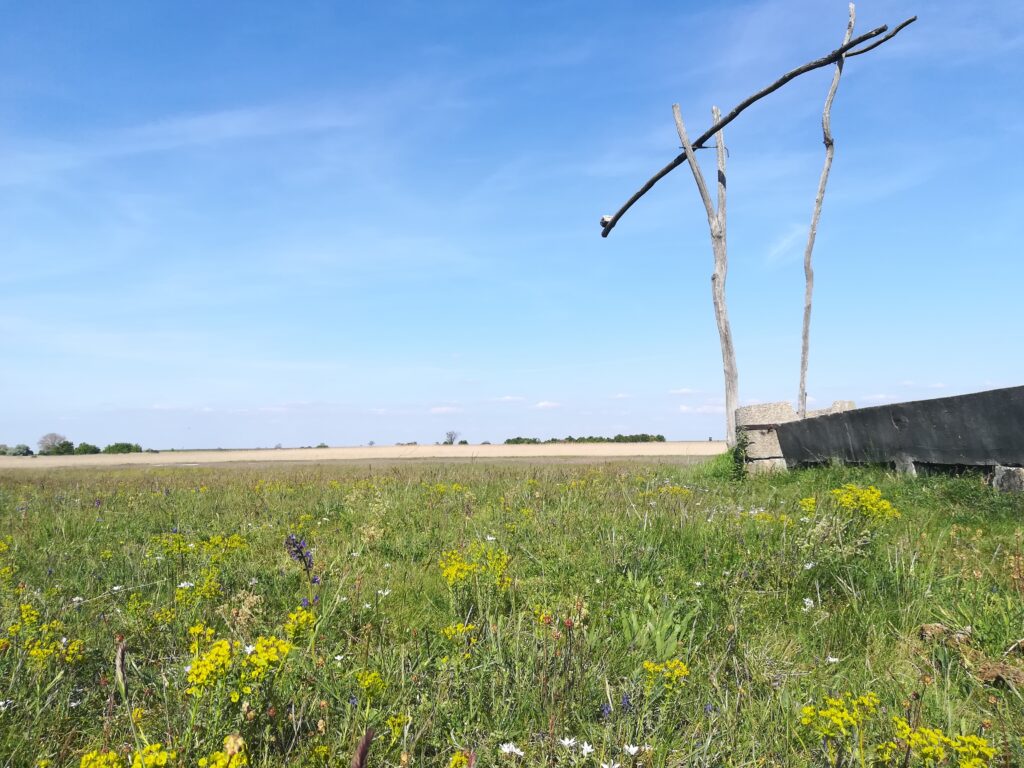

Austria – Neusiedler See – Seewinkel
In Austria, climate, topography and small-scale agriculture result in a large share of high nature value grassland. The national park “Lake Neusiedler See – Seewinkel” constitutes a steppe-like landscape, extremely rich in flora and fauna, threatened by eutrophication, changes in the water balance and intensification and abandonment, respectively, of extensive grasslands.
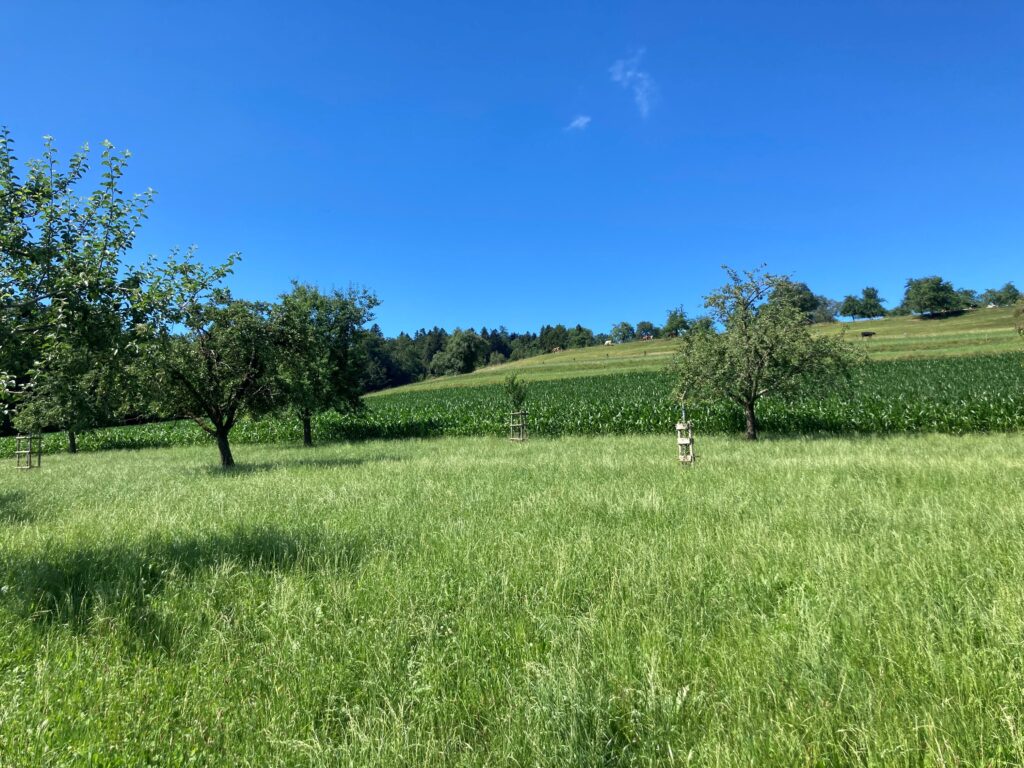

Switzerland – Grisons
In Switzerland only 13 % of the low-input meadows categorized as biodiversity priority areas are actually nutrient-poor species-rich meadows showing challenges to maintain those biodiversity hotspots. We use the area of the lower Engadine (Canton of Grisons) as a case study. This mountain region includes the “UNESCO Biosfera Engiadina Val Müstair” and borders the Swiss national park. In the Canton of Grisons intensification and abandonment of agriculture endangered 95% of protected dry grasslands since the start of the 20th century.
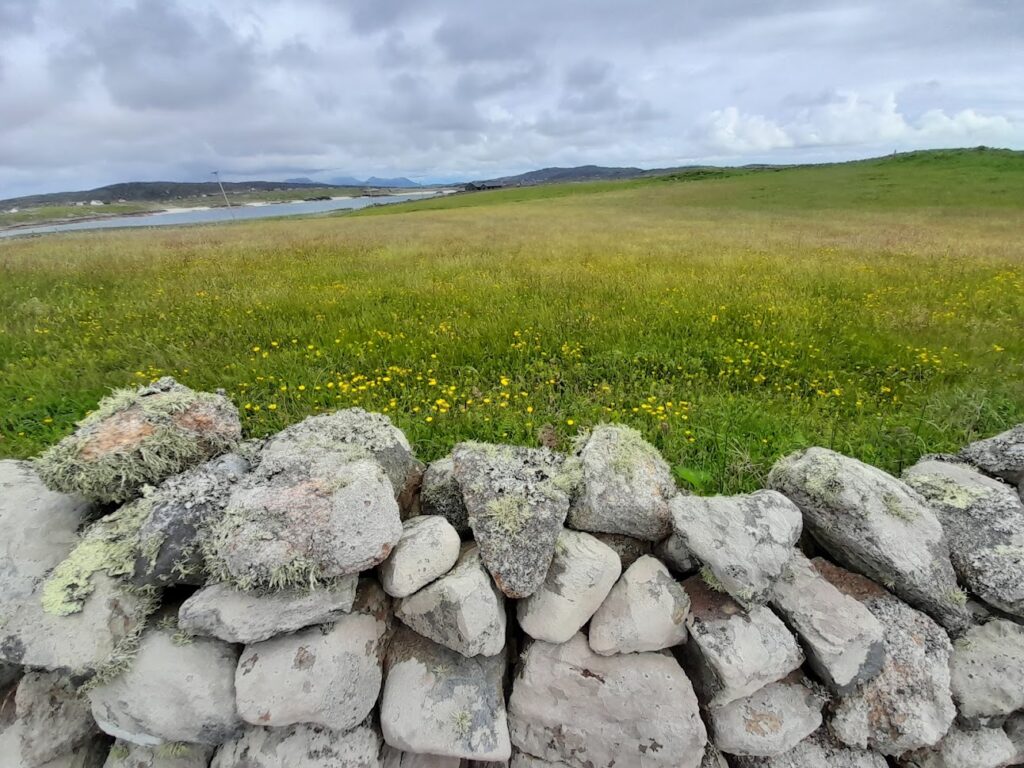

Ireland – North-West & West
In Ireland, grassland biodiversity plays a critical role for ecosystem services and economic sectors such as tourism. Major threats include farm intensification and specialisation, drainage, afforestation and land abandonment. The case study “West and North-West Ireland” covers a broad range of wet/dry lowland grasslands with appropriately structured ground vegetation. It faces both intensification and abandonment which threatens biodiversity such as the Corncrake (Crex crex).
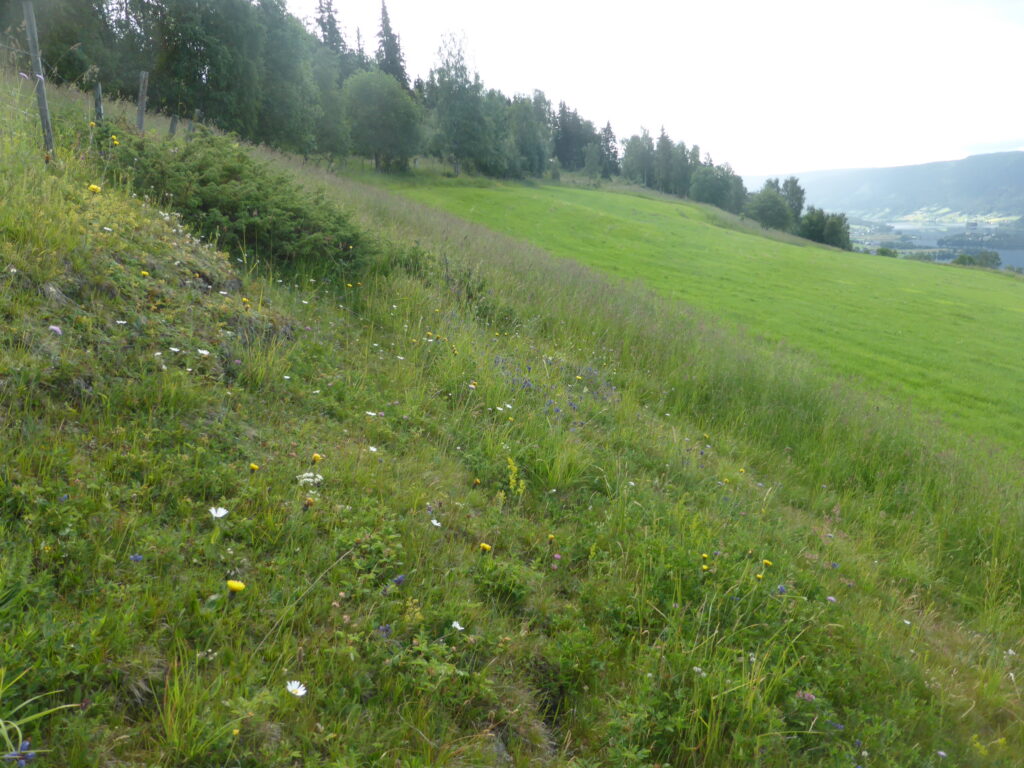

Norway – Valdres
In Norway, semi-natural grasslands are considered a threatened nature type mainly due to land-use change including both abandonment and management intensification. This has important biodiversity implications, as almost 25 % of nationally threatened species are found in semi-natural habitats, and therefore these areas are candidates for conservation. The Norwegian case study, situated in Valdres in Eastern Norway, constitutes a representative landscape with grassland ranging from intensively to extensively managed including traditional hay-meadows which are protected as “selected nature types”.

Germany – Havelland
In Germany, the nature park “Western-Havelland” integrates large scale SPA´s with several natura 2020 areas. High groundwater levels have formed landscapes dominated by a mosaik of fens, bogs, reets, permanent grasslands on organic fen soils and arable agriculture at sandy hills. The grassland use is at risk by abandonment and intensification at the same time with animal stocks continuously decreasing.

Estonia – Matsalu National Park
In Estonia the area of semi-natural habitats decreased dramatically due to either intensive cultivation or abandonment. The case study area is situated in the Matsalu National Park, mainly showing extensive grassland use.